Reserve Bank of Australia Annual Report – 2021Our Role
The Reserve Bank is Australia's central bank, as established under legislation. The Bank has five broad responsibilities:
- determine and implement monetary policy in pursuit of price stability and full employment
- foster the stability of the financial system
- support a secure, stable and efficient payments system
- deliver efficient and effective banking services to the Australian Government
- provide secure and reliable Australian banknotes.
The Bank's mission is to promote the economic welfare of the Australian people through our monetary and financial policies and operations. Our vision is to be a world-leading central bank that is trusted for our analysis, service delivery and policies. As part of our strategic plan, the Bank has six focus areas, which are outlined further in the Bank's Corporate Plan for 2021/22 to 2024/25.[1] The most important of these is for the Bank to continue to support the Australian economy in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. The other focus areas strengthen the capability of the Bank to deliver on its mission and key objectives successfully. The pursuit of our mission is also supported by our core values of promoting the public interest, integrity, excellence, intelligent inquiry and respect.
Reserve Bank of Australia Strategic Plan
August 2021
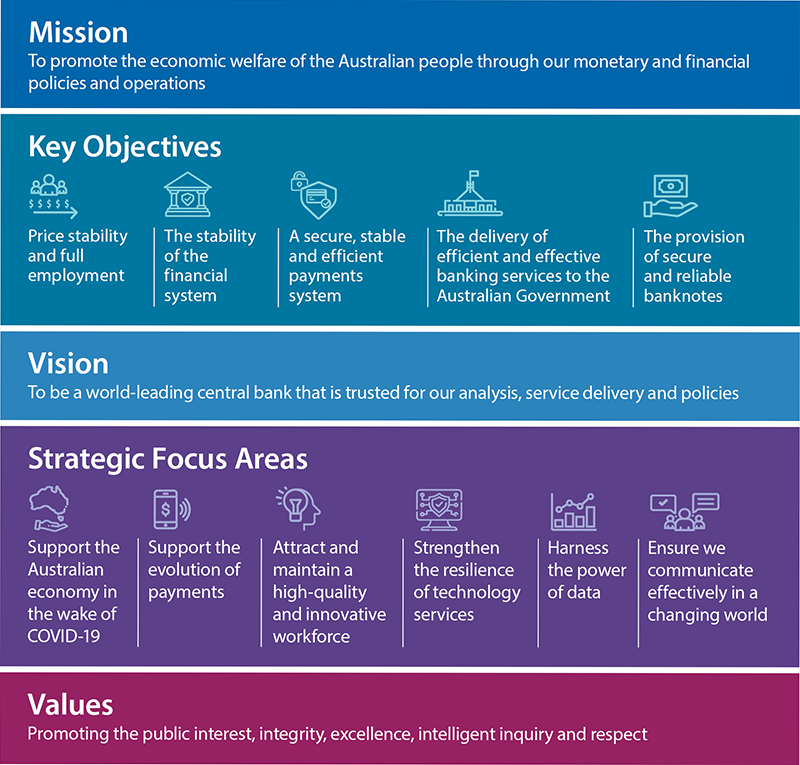
Price stability and full employment
The Bank's responsibility for monetary policy is set out in section 10(2) of the Reserve Bank Act 1959, which states:
It is the duty of the Reserve Bank Board, within the limits of its powers, to ensure that the monetary and banking policy of the Bank is directed to the greatest advantage of the people of Australia and that the powers of the Bank … are exercised in such a manner as, in the opinion of the Reserve Bank Board, will best contribute to:
(a) the stability of the currency of Australia;
(b) the maintenance of full employment in Australia; and
(c) the economic prosperity and welfare of the people of Australia.
Policies in pursuit of these objectives have found practical expression in a flexible, medium-term inflation target, which has formed the basis of Australia's monetary policy framework since the early 1990s. The policy objective is for consumer price inflation to average between 2 and 3 per cent over time. By achieving this objective, the Reserve Bank can help promote sustainable economic growth and employment.
The seventh Statement on the Conduct of Monetary Policy, agreed by the Treasurer and the Governor on 19 September 2016, records the common understanding of the government and the Reserve Bank on key aspects of the monetary policy framework.
The Reserve Bank conducts operations in domestic and international financial markets and undertakes analysis in support of its monetary policy objectives. The Bank conducts domestic market operations in support of the cash rate target, ensuring that there is sufficient liquidity in the domestic money market on a daily basis. Since March 2020, the Bank has also purchased government bonds in the secondary market in support of the Australian government bond yield target and the government bond purchase program, which were introduced as part of the Bank's comprehensive package of policy measures to support the Australian economy following the outbreak of COVID-19. As part of this package, the Bank also made available a term funding facility for the banking system.
The Bank also operates in the foreign exchange market to meet the foreign exchange needs of its clients (the largest of which is the Australian Government) and to assist with liquidity management in domestic markets. It holds and manages Australia's foreign currency reserves, and has the capacity to intervene in the foreign exchange market to address any apparent dysfunction in that market or significant misalignment in the value of the currency, consistent with the objectives of monetary policy.
The stability of the financial system
The Reserve Bank works with other regulatory agencies in Australia to foster overall financial stability, which is an important underpinning of a stable macroeconomic environment.
The Governor chairs the Council of Financial Regulators (CFR), a non-statutory coordinating body for Australia's main financial regulatory agencies, whose role is to promote the stability of the Australian financial system and support effective and efficient regulation by the financial regulatory agencies. Its members – the Reserve Bank, the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA), the Australian Securities and Investments Commission and the Australian Treasury – seek to identify issues that could affect financial stability, coordinate preparation for and responses to episodes of financial instability, and discuss financial regulation more generally.
Australia's financial stability policy framework includes mandates for financial stability for both APRA and the Reserve Bank. APRA is responsible for the prudential supervision of financial institutions, and has a broad mandate to promote financial system stability. The Bank is responsible for promoting overall financial system stability. In the event of a financial system disturbance, the Bank and relevant agencies work to mitigate the risk of systemic consequences. The Bank's responsibility to promote financial stability does not equate to a guarantee of solvency for financial institutions and the Bank does not see its balance sheet as being available to support insolvent institutions. Nevertheless, the Bank's central position in the financial system – and its position as the ultimate provider of liquidity to the system – gives it a key role in financial crisis management, in conjunction with the other members of the CFR.
A secure, stable and efficient payments system
The Reserve Bank has responsibility for ensuring the stability, efficiency and competitiveness of the payments system through the Payments System Board, which was established in 1998. The Bank's powers in relation to the payments system are set out in a number of statutes, including the Reserve Bank Act 1959, the Payment Systems (Regulation) Act 1998 and the Payment Systems and Netting Act 1998. Under the Corporations Act 2001, the Bank, through the Payments System Board, has responsibility for determining financial stability standards for licensed clearing and settlement facilities and assessing facilities' compliance with those standards.
The Reserve Bank also has an operational role in the payments system, as owner and operator of Australia's high-value real-time gross settlement system – the Reserve Bank Information and Transfer System (RITS). The Fast Settlement Service of RITS settles obligations arising from individual payments exchanged on the New Payments Platform in real time on a 24/7 basis. A separate area of the Bank assesses RITS against international standards for such infrastructure on an annual basis.
The delivery of efficient and effective banking services to the Australian Government
Insofar as the Commonwealth of Australia requires it to do so, the Reserve Bank must act as banker for the Commonwealth. The Reserve Bank's banking services fall into two components: those services provided in its capacity as the central bank; and those transactional banking services it provides to Australian Government agencies. In common with many other central banks, the Bank also provides banking and custody services to a number of overseas central banks and official institutions. The banking services offered to the Australian Government and other central banks include payments and collections as well as general account maintenance and reporting.
The provision of secure and reliable banknotes
The Reserve Bank is responsible for the issue, reissue and cancellation of Australian banknotes. Its primary purpose in carrying out this role is to maintain the capacity of Australian banknotes to provide a safe, secure and reliable means of payment and store of value. The Bank works with its wholly owned subsidiary, Note Printing Australia Limited (NPA), to design and produce banknotes. NPA also produces banknotes for other countries and Australia's passports. The Bank distributes banknotes to financial institutions, monitors and maintains banknote quality in circulation and withdraws unfit banknotes from circulation. It also monitors and analyses counterfeiting trends and conducts research into banknote security technology.
Endnote
See RBA (2021), ‘Corporate Plan 2021/22’. Available at <https://www.rba.gov.au/about-rba/corporate-plan.html>. [1]